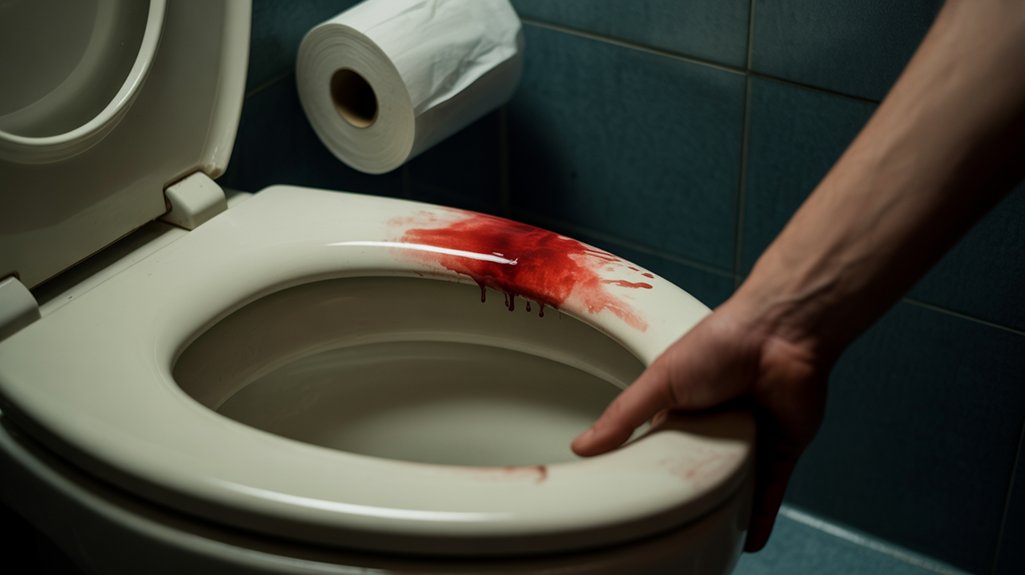
Blood in stool for men typically indicates bleeding somewhere in the digestive tract, with causes ranging from common hemorrhoids and anal fissures to more serious conditions like inflammatory bowel disease or colorectal cancer. The color provides important clues: bright red blood suggests lower tract bleeding, while dark or black stools indicate upper gastrointestinal issues. Men should seek immediate medical attention for severe symptoms including abdominal pain, fever, dizziness, or persistent bleeding, as proper diagnosis reveals the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.
Common Causes of Rectal Bleeding in Men
Blood in the stool, medically termed hematochezia when bright red or melena when dark and tarry, can stem from various conditions affecting different parts of the digestive tract. Hemorrhoids represent the most frequent culprit, causing bright red bleeding due to swollen blood vessels around the rectum. Hemorrhoid symptoms typically include itching, pain, and visible blood on toilet paper or in the bowl. Anal fissures, small tears in the rectal lining, produce similar bleeding patterns with sharp pain during bowel movements. More concerning gastrointestinal disorders include inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, and colorectal polyps or cancer. Upper digestive tract bleeding from ulcers or esophageal varices usually produces dark, tarry stools rather than bright red blood, indicating the blood has been digested during its journey through the intestinal system.
Identifying Different Types of Blood in Stool
Understanding the specific characteristics of blood present in stool helps medical professionals determine its likely source within the digestive system. Bright red blood typically indicates bleeding from the lower digestive tract, including the rectum, anus, or sigmoid colon. Dark red or maroon-colored blood suggests bleeding from the middle portion of the colon, while black, tarry stools often signal upper gastrointestinal bleeding from the stomach or small intestine.
Stool Color Analysis
Medical experts examine stool color patterns to assess bleeding significance and urgency. Fresh blood streaks on toilet paper usually indicate minor anal fissures, whereas blood mixed throughout the stool suggests more serious internal bleeding. Dr. Sarah Chen, gastroenterologist, explains that “the appearance, amount, and consistency of blood provides vital diagnostic clues about the underlying condition’s severity and location.”
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Recognizing warning signs that demand immediate medical intervention can be lifesaving when blood appears in stool, as certain symptoms indicate potentially serious complications requiring urgent treatment.
Critical Emergency Symptoms
Severe abdominal pain accompanied by bloody stools requires immediate emergency care, particularly when combined with fever, dizziness, or rapid heartbeat. According to gastroenterologist Dr. Michael Chen, “Heavy bleeding with clots, weakness, or fainting signals potential hemorrhage requiring urgent intervention.”
Effective Symptom Monitoring
Men should track bleeding frequency, color changes, and associated symptoms for accurate urgency assessment. Bright red blood with severe cramping, vomiting blood, or black tarry stools warrant emergency room visits. Dr. Sarah Martinez notes, “Don’t wait when bleeding persists beyond 24 hours or increases in volume, as delayed treatment can lead to serious complications.”
Diagnostic Tests and Medical Evaluation
Once a patient presents with concerning symptoms to a healthcare provider, medical professionals employ a systematic approach to identify the underlying cause of rectal bleeding through various diagnostic procedures. The initial symptom assessment involves detailed questioning about bleeding patterns, stool consistency, pain levels, and associated symptoms like weight loss or fatigue.
Blood analysis represents a fundamental diagnostic tool, revealing essential information about hemoglobin levels, white blood cell counts, and inflammatory markers that indicate infection or systemic disease. Additional tests may include colonoscopy, which allows direct visualization of the colon’s interior, CT scans for detecting structural abnormalities, and stool cultures to identify bacterial infections. These thorough evaluations enable physicians to distinguish between minor issues and serious conditions requiring immediate intervention.
Treatment Options and Prevention Strategies
Effective treatment for rectal bleeding varies dramatically based on the underlying cause, ranging from simple dietary modifications to complex surgical interventions. Hemorrhoids often respond well to over-the-counter creams, sitz baths, and increased fiber intake, while inflammatory bowel disease may require prescription medications like immunosuppressants or biologics.
Lifestyle changes play an essential role in prevention and management. Regular exercise, adequate hydration, and stress reduction techniques help maintain digestive health. Dietary adjustments prove particularly beneficial, including adding high-fiber foods like beans, whole grains, and vegetables while limiting processed foods and excessive red meat consumption.
Severe conditions such as colorectal cancer necessitate extensive treatment plans involving surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. Early intervention greatly improves outcomes, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical evaluation when blood appears in stool.